Table of Contents
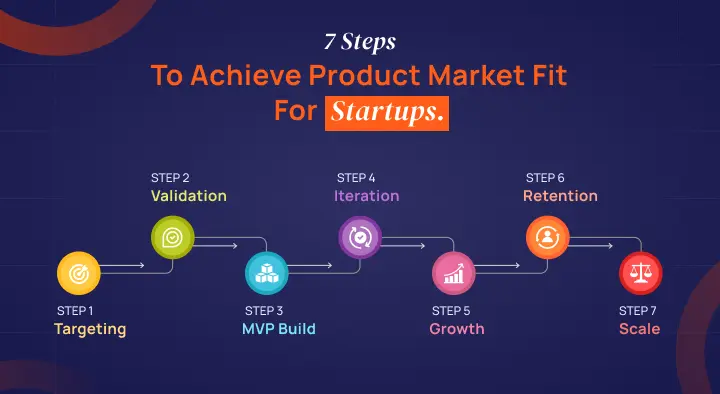
- 7 steps to achieve product market fit for startups.
- Step 2: Validate Your Problem for Achieving Product Market Fit
- Step 3: Build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
- Step 4: Test, Learn & Iterate: A must-step to achieve product-market fit
- Step 5: Find Your Growth Channels
- Step 6: Retention Over Acquisition
- Step 7: Scale Responsibly After PMF
- Common Mistakes Startups Make While Chasing PMF
- Final Thought
- FAQs
Every startup begins with an idea, but only the ones that achieve product-market fit (PMF) become real businesses. The importance of PMF matters to every startup, yet just knowing that and measuring it isn't enough. It is essential to know how to achieve a product-market-fit framework to build solutions, as that's when your real journey begins. If you are aiming to build a genuine value solution, your startup needs clarity, fast learning, and a strong product-market fit framework. This guide breaks down the real path to product-market fit. Not a theory, but a process broken into simple, impactful, actionable steps so you can move from assumptions to actual customer demands. In the end, it is all about achieving product-market fit.

Step 1: Identify a Clear Target Audience for Your Product
Imagine two founders. Founder A builds a product for everyone, and founder B builds for one clearly defined user with a specific pain point and a reason to pay. Who wins? Founder B. Start by:
- You have to start the product market fit process by defining exactly who you are building for.
- Create a sharp Ideal Customer Profile (ICP), including age, behavior, goals, buying power, and challenges.
- Understand what they struggle for.
- Understand the market with market research to uncover real pain points, unmet needs, and patterns that shape user-product fit.
- Use these insights from market research to take the next step in product strategy and ensure it aligns with true market resonance.
- Next, validate early assumptions through customer validation methods such as interviews, surveys, and rapid MVP testing. Consider it the first of the core steps to achieve product-market fit. Set the foundation for all later product iteration loops.
- Strong audience clarity supports value proposition validation, early startup traction, and long-term startup growth.
- A well-defined ICP reduces risk during business model validation and prepares you for the later stages of product market fit and business scaling.
Step 2: Validate Your Problem for Achieving Product Market Fit
If users don’t care about the problem, they won’t care about your product. Founders fall in love with solutions. Successful founders fall in love with problems. Now you have to validate:
- Start with baby steps, like the product market fit validation stage, by running deep customer-discovery interviews.
- Listen for real frustrations and not just polite answers.
- You have to identify if the pain is urgent or just a “nice-to-have.”
- Strong problem validation boosts value proposition validation, startup traction, and sharper product strategy.
- This step answers a key PMF question: How to find the right audience for product-market fit?
Step 3: Build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Many startups spend months building the perfect version of a product. And then the user goes and says, “Cool idea, but it is not what I need.”
A good MVP isn’t a smaller version of your dream. It’s the smallest thing that proves value.
- Build a focused MVP that solves one core problem identified earlier.
- Avoid overbuilding; stay aligned with the lean startup mindset.
- Your MVP should reflect the strongest insight from user feedback, market research, and the early product validation process.
- Successful MVP testing helps you understand “how do I know if my product has market fit?”
- A tight MVP accelerates the early stages of product market fit and prepares you for fast product iteration loops.
Step 4: Test, Learn & Iterate: A must-step to achieve product-market fit
Your first launch won’t be perfect. It isn’t supposed to be. Collect feedback. Measure usage. Watch behavior, not compliments. Then improve. Then test again.
- Keep on running small experiments to test assumptions and measure market resonance.
- Collect all early data through surveys, NPS, interviews, and retention curves.
- Use fast iteration cycles—build → test → learn—following the Lean Startup method.
- These loops reduce risk, increase clarity, and support startup growth.
- This phase explains what strategies help startups achieve PMF faster.
Step 5: Find Your Growth Channels
Traction doesn’t come from being everywhere. Great products grow where the customers already exist.
- Identify where your ICP actually spends time; this is key to the product market fit process.
- Conduct tests on multiple acquisition channels: SEO, paid ads, influencers, community, and partnerships.
- Always keep track of early traction and double down on the one scalable channel once PMF signals appear.
- Clear channel focus supports business model validation and long-term business scaling.
- This step answers: What are the steps to achieve product-market fit?
Try multiple channels. Then double down on what brings recurring users. All you need is one channel working well for you. You can grow on other channels in parallel.
Step 6: Retention Over Acquisition
PMF isn’t about someone signing up. PMF is when people return because they love the product. So, focus on this.
- For any startup, retention is one of the strongest signs of true product market fit.
- Focus on onboarding, product experience, engagement loops, and habit-building features.
- Use metrics like DAU/MAU, churn rate, repeat usage, and customer sentiment to measure the depth of value.
- For a budding start-up, strong retention gives clarity on what the signs are that you’ve achieved product-market fit.
Step 7: Scale Responsibly After PMF
Premature scaling is like adding fuel to a car with no engine. And this is one of the top reasons startups run out of cash.
- You have to remember, do not scale before PMF is solid. Because premature scaling kills momentum.
- Focus on strengthening product quality, customer success, operations, and tech stability.
- You can use the PMF-to-Growth Flywheel: value → retention → referrals → traction → scaling.
- This stage ensures you’re achieving growth-stage readiness and unlocking sustainable startup traction.
- Also clarifies: How long does it take to achieve product-market fit? (It varies, but scaling begins only after strong PMF signals.)
Once you have covered all your bases, then scale with confidence, not hope. When you scale, scale with insights. How? Read our guide on “How to Measure Product-Market Fit.”
Common Mistakes Startups Make While Chasing PMF
Each entrepreneur loves to solve people’s problems. But while doing so, they make the most common mistakes that stop them from building successful companies.
- Building for everyone
If you are building for everyone, then your product won’t be successful. Windows was built for computers but couldn’t be replicated for Android.
It is impossible to make everyone happy, and ultimately, no one stays happy in that race. PMF requires a sharp focus on one audience segment. Clear ICPs and tight customer validation are essential for strong market resonance. - Misreading data or scaling too early
Vanity metrics mislead you. Many founders expand teams, operations, or marketing before completing the real product market fit validation. True PMF shows up in retention, repeat usage, and deep value adoption, and not just in clicks or downloads. - Ignoring user feedback
Feedback loops fuel the product iteration loop, MVP testing, and early stages of product market fit. When founders avoid uncomfortable insights, they delay PMF and slow startup growth. Feedback shows the direction you have to walk.
Final Thought
The journey of how to achieve product market fit is not luck. It is a disciplined, repeatable path. It’s earned with conversations, experiments, customer obsession, and the courage to refine—again and again.
When founders follow the steps to achieve product market fit, validate the problem, build a sharp MVP, test fast, and scale responsibly, they unlock real demand and long-term traction. These seven steps form the backbone of a strong product market fit process, guiding you through every stage from early discovery to confident scaling.
If you want guidance on achieving your PMF, you can reach out to us, Mr CEO, for a one-on-one mentorship with our mentors.
FAQs
1. What is Product-Market Fit (PMF)?
Product-Market Fit is the stage when a startup has found a good market (a large group of people with a similar, urgent pain point) and built a product that satisfies that market’s needs. PMF is when customers return and use the product repeatedly because they genuinely love it and find it essential, not just when they sign up for the first time.
2. What are the strongest indicators that a startup has achieved PMF?
The strongest indicator of true PMF is retention, when people keep coming back to use the product. Key points to track:
- High Repeat Usage: Customers are using the product habitually.
- Low Churn Rate: Users are not leaving the product.
- Strong Engagement Metrics: High Daily Active Users (DAU) to Monthly Active Users (MAU).
- Customer Sentiment: Users express deep value adoption and would be upset if the product disappeared (often measured via tools like NPS surveys).
3. How soon should a startup begin scaling operations and marketing?
Startups should only scale after PMF is solid. Premature scaling is one of the top reasons startups run out of cash and lose momentum. You must first focus on strengthening the product, customer success, and operational stability to support the PMF that has already been validated.
4. What is an MVP, and what should be its main focus?
An MVP (Minimum Viable Product) is the smallest, most focused version of a product that proves value by solving one core problem for the clearly defined target audience. Its main focus should not be on being a smaller version of the dream product but on being the smallest thing required to validate the core value proposition and gather early, essential feedback from the target market.
5. Why is it a mistake for a startup to “Build for everyone”?
Building for everyone is a critical mistake. PMF required a sharp focus on one audience segment. This way product can benefit x number of customers for A problem. When you target everyone, people who don’t have A problem, they will not use it. And that is where the companies’ loss lies.